Handholding them with care and appropriate. Medical advices.
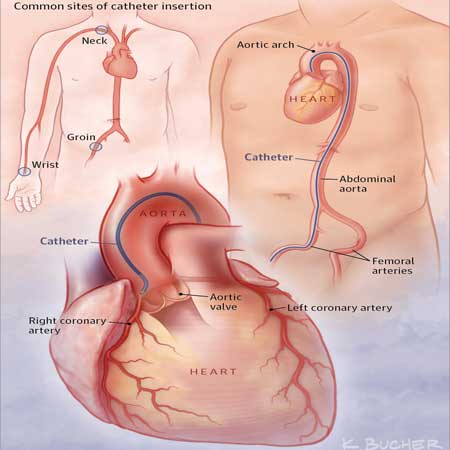
Minimally Invasive CABG Surgery
Minimally Invasive Hybrid Coronary Revascularisation Surgery (MIHCR)
Minimally Invasive Aortic Valve Replacement